Learning-Induced Channel Extrapolation for Fluid Antenna Systems Using Asymmetric Graph Masked Autoencoder
Published in IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2024
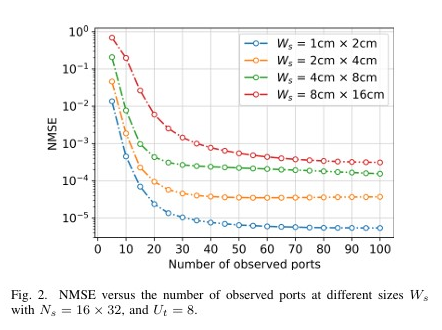
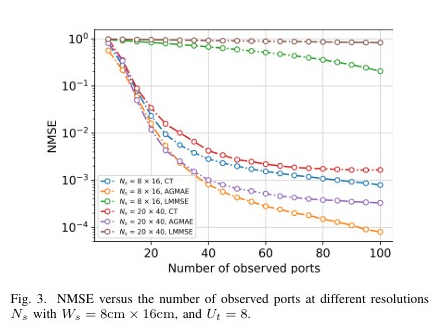
Abstract:The emerging fluid antenna systems (FASs) enable position-flexible antennas that provide a new degree of freedom for more diversity and multiplexing benefits. However, the challenge for high-resolution FAS is the acquisition of complete and accurate channel state information (CSI) within a coherence time period. In this correspondence, we study deep learning methods for CSI extrapolation in high-resolution FAS with less complexity and greater generalization ability. In so doing, we then contrive a customized solution, referred to as an asymmetric graph masked autoencoder (AGMAE), specifically designed for spatial channel extrapolation in FAS. This technique incorporates an attention mechanism, an asymmetric masked autoencoder architecture to reduce computational complexity, and utilizes the local diffusion mechanism of graph neural networks to enhance generalization. Simulation results validate the effectiveness and generality of the proposed method for the CSI acquisition of FAS. Index Terms: Asymmetric graph masked autoencoder, channel extrapolation, channel state information, fluid antenna systems.
Recommended citation: Zhang, Haibin, et al. "Learning-induced channel extrapolation for fluid antenna systems using asymmetric graph masked autoencoder." IEEE Wireless Communications Letters (2024).
Download Paper
